Diabetes types, symptoms, causes and treatment
Diabetes explained: Types, symptoms, causes, tests, treatment and prevention
- By Gurmehar --
- Friday, 22 Aug, 2025
Diabetes is one of the fastest-growing health problems in the world, including in India. It happens when the body cannot properly use or make enough insulin, the hormone that helps move sugar (glucose) from the blood into the cells for energy.
When this process does not work, sugar stays in the blood. Over time, this can harm the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. Diabetes is a lifelong condition, but with the right care, it can be managed.
Understanding diabetes and its main types
Diabetes is a long-term condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal. There are three main types:
-
Type 1 diabetes: Usually starts in children or young adults. It is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system destroys the insulin-making cells in the pancreas. People with Type 1 diabetes need daily insulin injections to survive.
-
Type 2 diabetes: The most common type, often linked to being overweight, family history, or lack of exercise. The body makes insulin but cannot use it properly. It can be managed with healthy eating, exercise, medicines, or sometimes insulin.
-
Gestational diabetes: Develops during pregnancy when hormones affect the way insulin works. It usually goes away after birth but increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes later for both mother and child.
Rising diabetes cases in India
India now has over 100 million people living with diabetes. Urban areas report higher rates, but rural areas are catching up quickly. Younger people and even children are also being diagnosed more often, making it a growing public health concern.
Why diabetes is increasing in young people
-
Family history of diabetes
-
Sedentary lifestyle and less exercise
-
Weight gain and unhealthy diets
-
Stress and poor sleep habits
When young people develop diabetes, the disease can be more aggressive, with complications appearing sooner in life.
Symptoms, causes, tests, and prevention
Early warning signs of diabetes
Some symptoms are obvious, while others are subtle:
-
Frequent urination, especially at night
-
Excessive thirst
-
Tiredness or fatigue
-
Blurred vision
-
Unexplained weight loss
Other silent symptoms, especially in women and older adults, may include frequent infections, slow-healing wounds, tingling in the hands and feet, or mood changes.
Causes and risk factors
-
Genetics: Family history increases the chances.
-
Lifestyle: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and alcohol raise risks.
-
Obesity: Extra weight, especially around the belly, causes insulin resistance.
-
Stress and sleep: Chronic stress and poor sleep make it harder for the body to regulate blood sugar.
ALSO READ: Zelenskyy pushes US for stronger security guarantees before agreeing to Russia peace deal
ALSO READ: Punjab government saves ₹383 crore, empowers 10,000 teachers with AI training
Complications of untreated diabetes
If diabetes is not controlled, it can cause:
-
Eye damage (retinopathy) – leading to vision loss.
-
Kidney disease – eventually causing kidney failure.
-
Heart disease – increasing the risk of heart attack or stroke.
-
Nerve damage – causing pain, numbness, or infections in the feet.
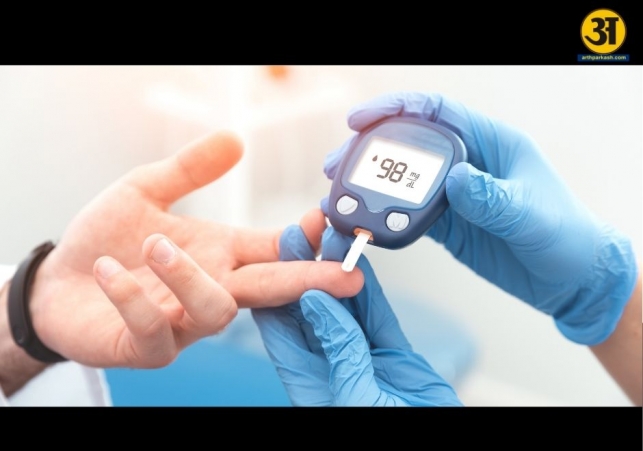
How diabetes is diagnosed
Doctors check for diabetes using blood tests:
-
Fasting Blood Sugar Test – after not eating for 8 hours. A level of 126 mg/dl or more suggests diabetes.
-
HbA1c Test – shows average blood sugar levels over 2–3 months. A result of 6.5% or more confirms diabetes.
-
Random Blood Sugar Test – taken any time; 200 mg/dl or higher indicates diabetes.
Cost of tests in India
-
Fasting/Random blood sugar: ₹100–200
-
HbA1c: ₹400–800
These tests are widely available in labs and hospitals, and often at health camps for low or no cost.
Managing and preventing diabetes
Treatment and lifestyle management
There is no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed with:
-
Healthy diet – Focus on vegetables, whole grains, pulses, lean protein, and limit sugary foods, white rice, and fried items.
-
Exercise – Regular walking, yoga, or sports help the body use insulin better.
-
Medicines/insulin – As prescribed by the doctor.
-
Regular monitoring – Checking blood sugar at home or in labs.
For women, conditions like PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) and gestational diabetes make regular screening even more important.
Home and Ayurvedic support (complementary care)
Some natural remedies can support blood sugar control (but should not replace medicines):
-
Fenugreek seeds (methi) – soaked overnight and taken in the morning.
-
Cinnamon – may improve insulin sensitivity.
-
Jamun (Indian blackberry) – seeds and fruit can help slow sugar absorption.
-
Giloy – an Ayurvedic herb that may support sugar balance.
Always consult a doctor before starting home remedies.
Prevention tips for high-risk people
If you are at risk of diabetes, you can delay or even prevent it with simple changes:
-
Maintain a healthy weight – Even a 5–7% weight loss reduces risk.
-
Exercise regularly – 30 minutes of activity most days.
-
Eat balanced meals – More fibre, fewer processed foods.
-
Sleep well and manage stress – Both affect blood sugar.
-
Regular check-ups – Early detection can prevent serious complications.
Living well with diabetes
A diabetes diagnosis can feel overwhelming, but millions of people live healthy, active lives with it. Celebrities like Nick Jonas, Sonam Kapoor, and Tom Hanks openly share their diabetes journey to inspire others.
The key is consistency:
-
Follow your doctor’s advice.
-
Stay active and eat balanced meals.
-
Monitor blood sugar regularly.
-
Take care of mental health—stress management is as important as diet and exercise.
Diabetes may not have a cure, but with awareness, lifestyle changes, medical care, and early detection, you can live a long, fulfilling, and healthy life.





